####: ##########
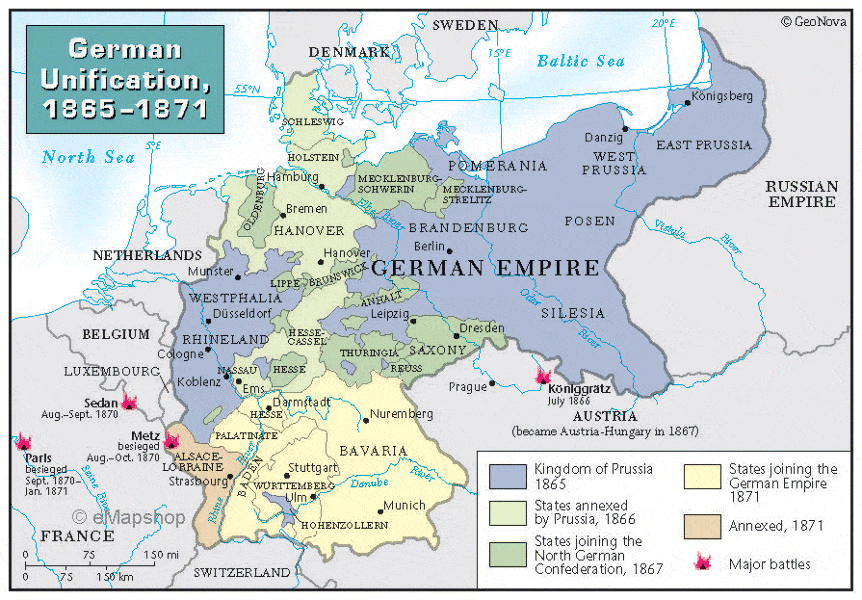
Germany unified officially into a nation state in 1871, but the process of unifying the various German states into one had been a developing process over many years. Through diplomacy and war, a once fragmented peoples united to form the German nation...

The Holy Roman Empire, a complex of territories consisting of many German territories, was dissolved during the Napoleonic Wars. Much of the empire was reorganized into the Confederation of the Rhine, a French satellite.
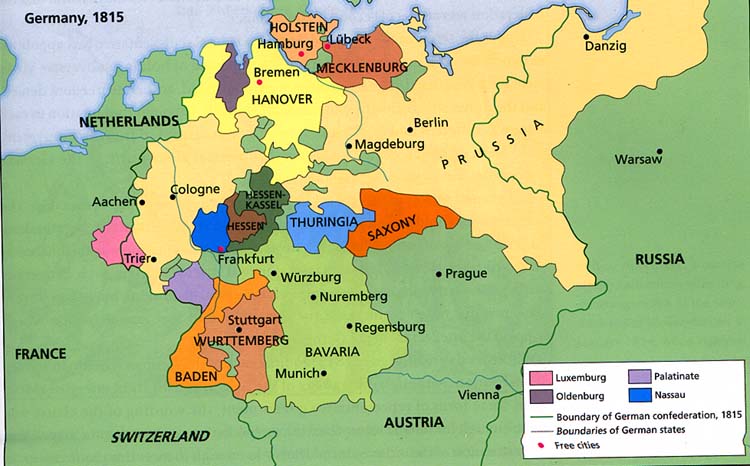
With the conclusion of the Napoleonic Wars with the Treaty of Vienna, borders and states were reorganized to restore the balance of power in Europe. The German states became the German Confederation with its two most prominent members being Austria and Prussia.
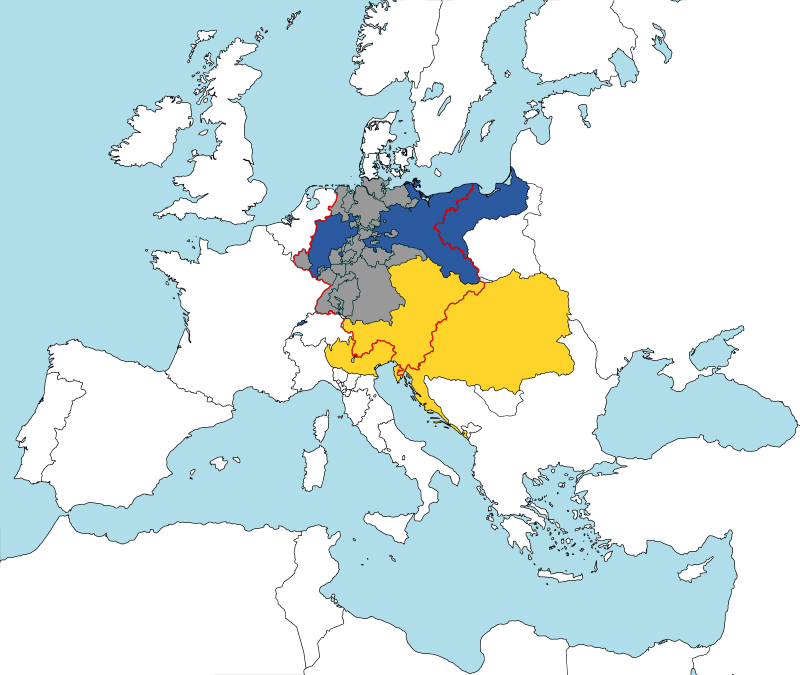
Prussia created The Zollverein or German Customs Union, a coalition of German states, to increase economic unity among the German states. The Zollverein managed tariffs and economic policies. Austria was not a member of the organization.
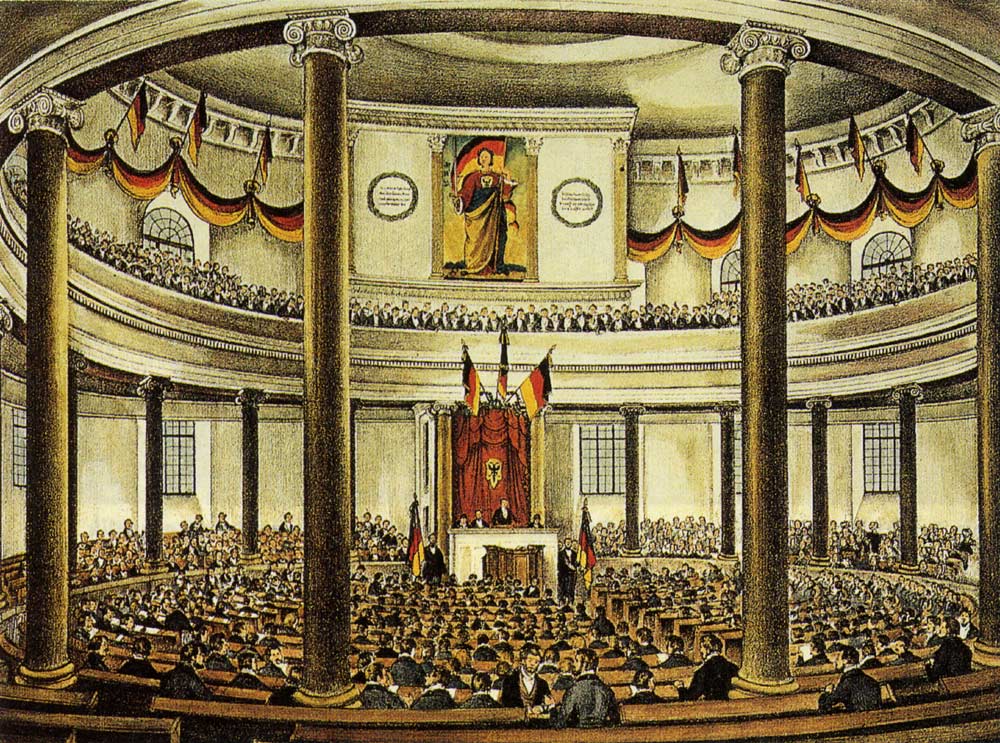

The Frankfurt Parliament of 1848 was the first freely elected parliament for all of Germany. At the assembly, the Frankfurt Constitution was produced, proclaiming a German Empire that would practice parliamentary democracy to meet the demands of the liberal and nationalist movements. The Prussian King Frederick William IV rejected the offer of emperor.

Otto von Bismarck was appointed as Prime Minister and Foreign Minister in 1862. Through his diplomacy, the German Empire became a dominant power in continental Europe. Soon after his apointment as Prime Minister, Bismarck made his famous "Iron and Blood" speech explaining Prussia's willingness to use "iron and blood" to achieve its goals.

The German Confederation was divided in the Austro-Prussian War as Prussia and Austria each led their own allies from the German Confederation into war. Prussia emerged victorious from the brief war, thus shifting the power among the German states toward Prussia, which would be instrumental in German unification. The German Confederation was abolished.
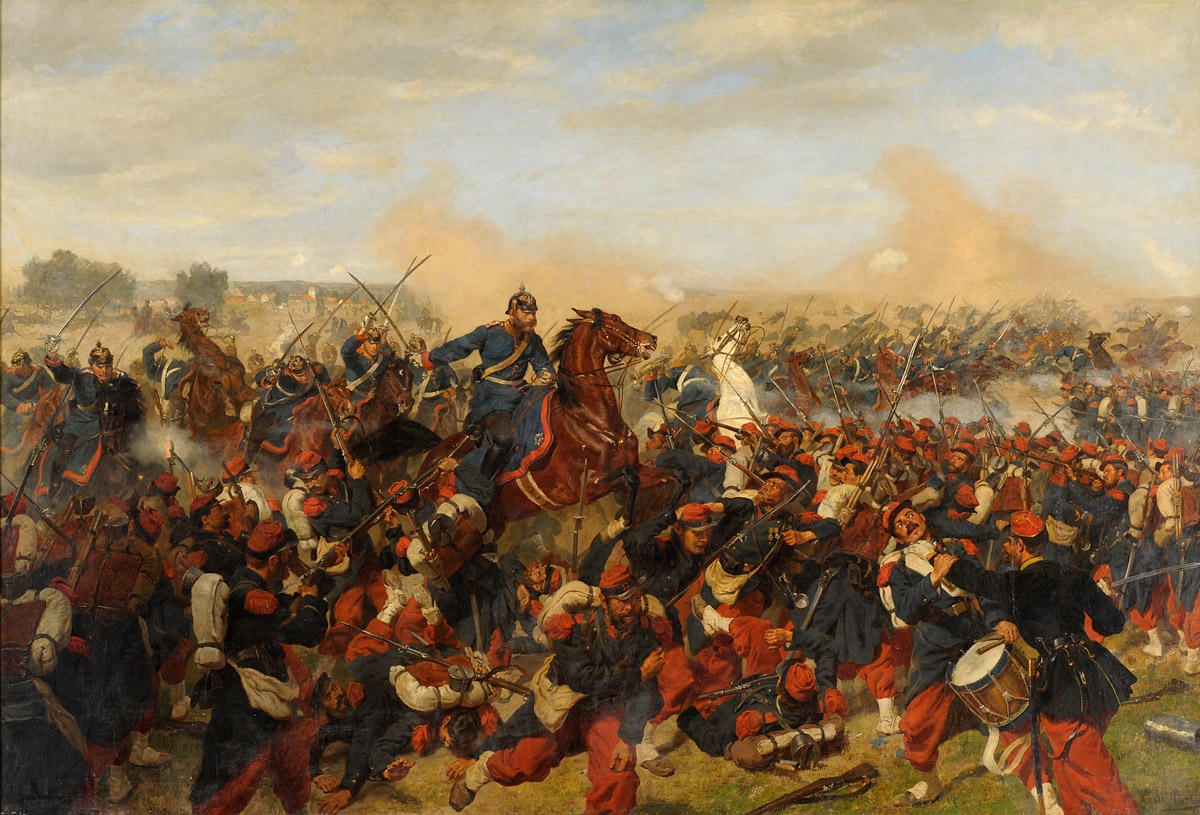

Provoked by Otto von Bismarck, France declared war on the German Kingdom of Prussia, initiating the Franco-Prussian War. The North German Confederation led by Prussia quickly defeated France culminating in the Siege of Metz and the Battle of Sedan. The war gave Germany the French territory of Alsace-Lorraine, and Germany was further pushed towards unity under Prussian dominance.

The Austro-Prussian War and Franco-Prussian War bothed proved Prussia's ability to lead the German states. With the conclusion of he latter war, Prussia's hegemony was clearly defined, and the German states were organized into a unified Germany with the Treaty of Versailles of 1871. The German nation had been born...